Vitiligo
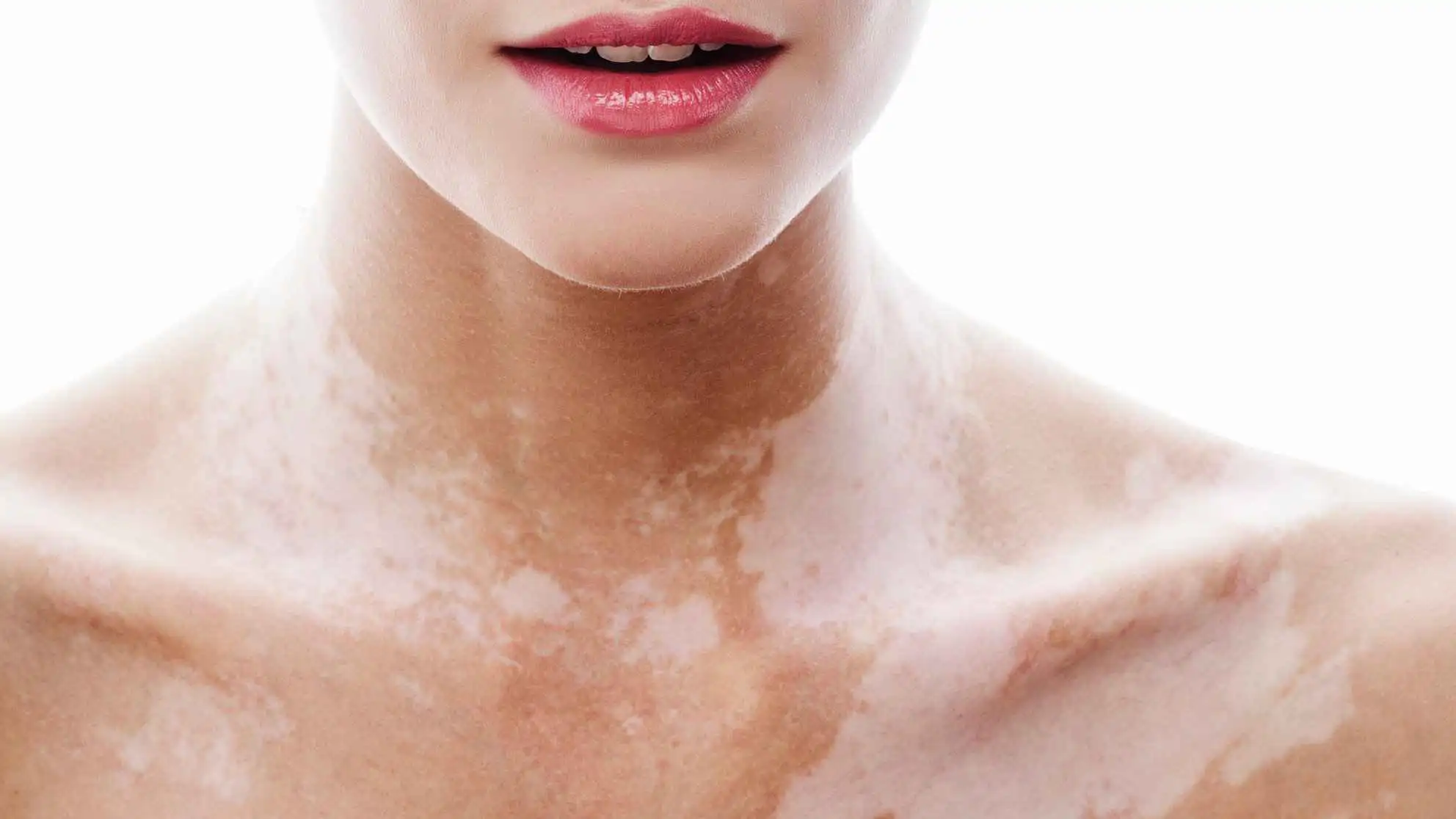
Vitiligo
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition in which the skin loses its natural pigment (melanin), leading to the development of white or depigmented patches on different parts of the body. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes.
What's Included
Dermatologist’s Perspective:
- Autoimmune Cause: Vitiligo is considered an autoimmune condition where the immune system targets melanocytes.
- Not Contagious: Vitiligo is non-infectious and non-contagious.
- Psychological Impact: The visible nature of vitiligo can affect emotional and psychological well-being, especially in darker skin tones.
- May Be Hereditary: A family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune diseases can increase risk.
Common Sites Affected
- Face and around the eyes or mouth
- Hands and fingers
- Feet, elbows, knees
- Genitals or body folds
- Scalp (may cause white/gray hair)
Types of Vitiligo
- Segmental Vitiligo: Affects only one side or segment of the body; usually starts at a younger age.
- Non-segmental (Generalized) Vitiligo: The most common type; symmetrical white patches appearing on both sides of the body.
- Focal Vitiligo: Limited to a few isolated patches.
- Universal Vitiligo: A rare form that causes widespread depigmentation.
Diagnosis
-
Diagnosis is made through clinical examination by a dermatologist. A special UV light called a Wood’s lamp may be used to highlight affected areas. In some cases, a skin biopsy or blood tests may be recommended.
Treatment Options
- Topical medications: Corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors to stimulate pigment production.
- Phototherapy: Narrowband UVB therapy is the most common and effective light-based treatment.
- Excimer laser: Targeted light treatment for smaller patches.
- Surgical options: Skin grafting or melanocyte transplantation for stable vitiligo.
- Camouflage cosmetics: Special makeup or dyes to even out skin tone.
- Depigmentation therapy: For extensive cases, remaining pigmented skin may be lightened to match affected areas.
Important Notes
- Vitiligo is a long-term condition with unpredictable progression.
- It may be associated with other autoimmune diseases like thyroid disorders or diabetes.
- Sun protection is essential to prevent sunburn in depigmented areas.
Medicine Use Disclaimer: The above information is for educational purposes only. Do not start any treatment or medication without consulting a qualified dermatologist. Individual treatment plans vary based on the cause, severity, and progression of the condition.
