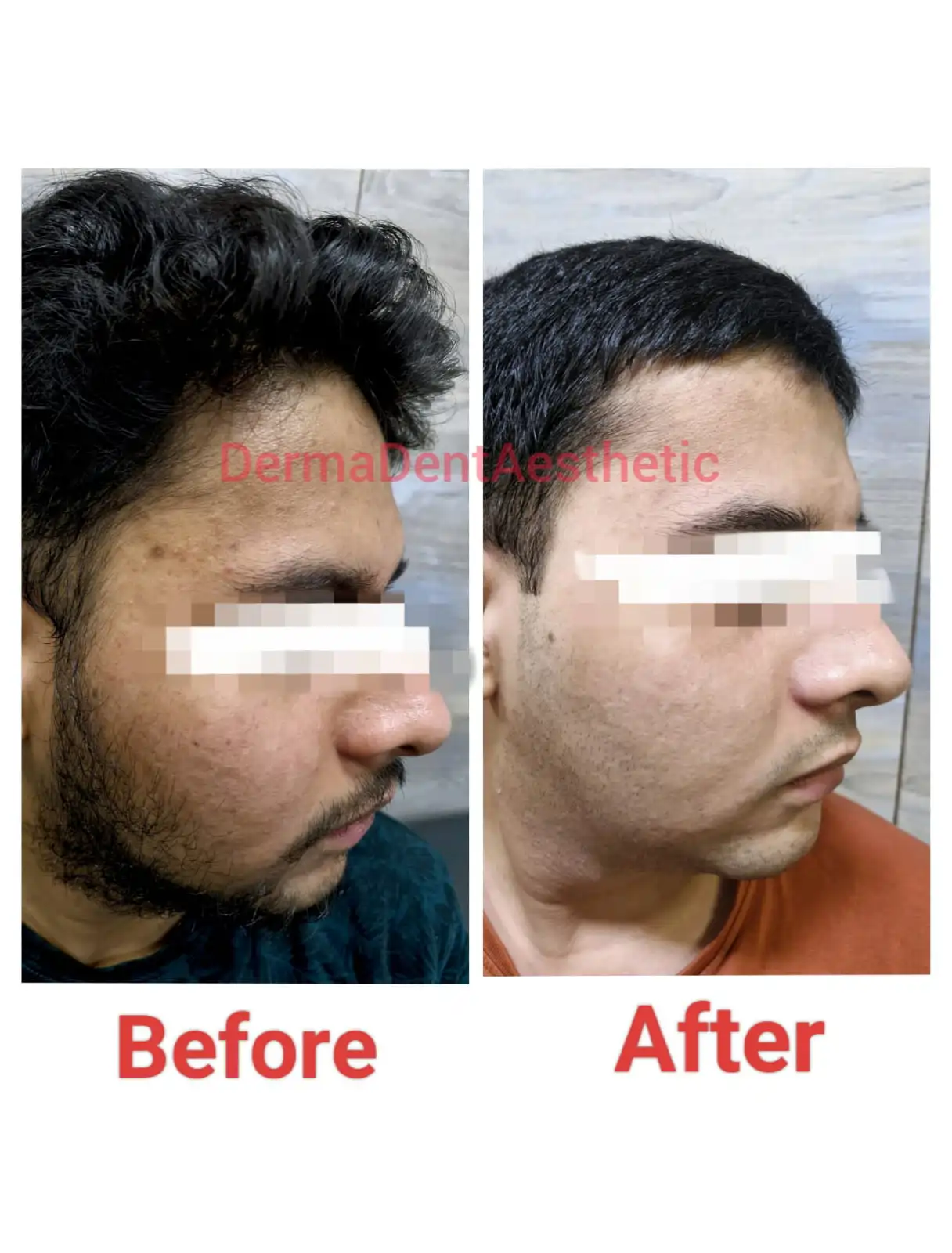
Skin Pigmentation
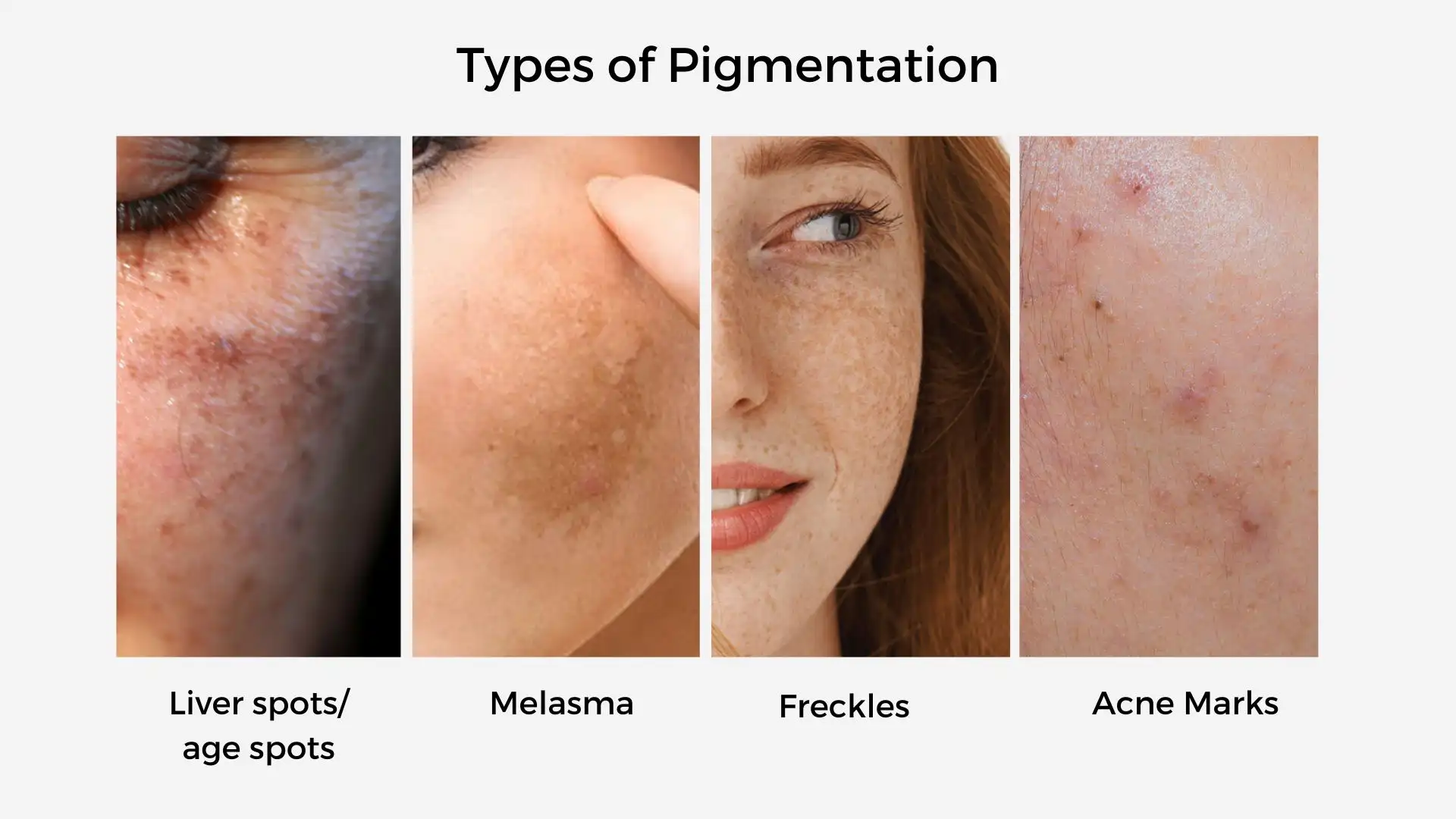
Skin Pigmentation
What is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the color of your skin, determined by the amount of melanin—a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. Changes in pigmentation can result in patches that are lighter (hypopigmentation) or darker (hyperpigmentation) than the surrounding skin.
What's Included
Common Causes of Pigmentation:
- Excess sun exposure (UV rays)
- Hormonal changes (e.g., melasma during pregnancy)
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (acne, injuries)
- Genetics and skin type
- Certain medications or cosmetics
Types of Pigmentation Disorders:
- Melasma: Brown patches on face, often hormone-related
- Freckles: Small brown spots, usually from sun exposure
- Solar Lentigines: Also called age spots or liver spots
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark marks left after acne or injury
- Vitiligo: Loss of melanin resulting in white patches
Treatment Options:
- Topical creams: Hydroquinone, retinoids, azelaic acid
- Chemical peels: Glycolic acid, salicylic acid
- Laser treatments: Q-switched lasers, fractional lasers
- Microneedling with serums
- Sun protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum SPF 30+
Disclaimer: Do not self-treat pigmentation with over-the-counter products without consulting a qualified dermatologist. Improper use can worsen the condition or cause skin damage.