Alopecia
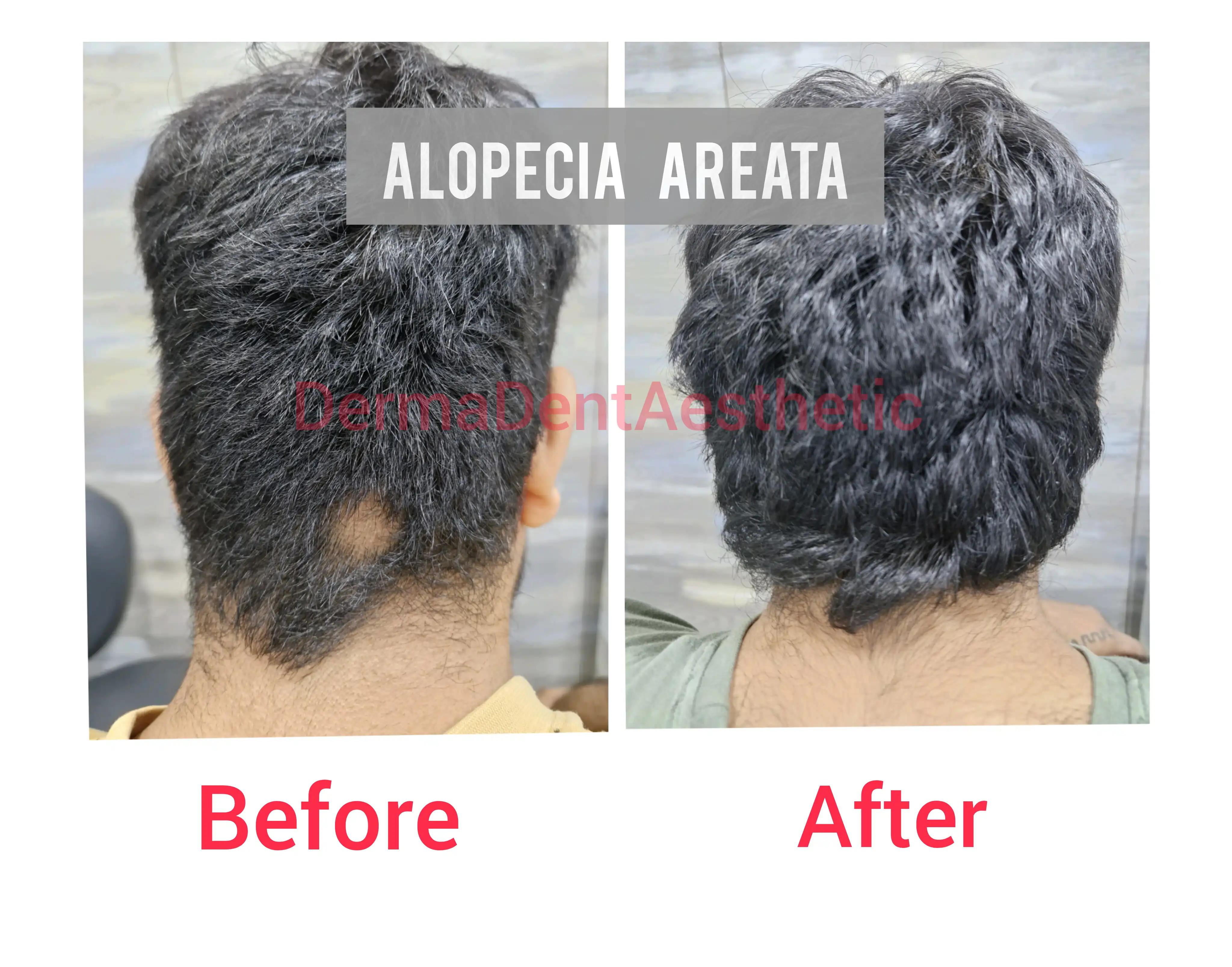
Alopecia
What is Alopecia?
Understanding Alopecia
"Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss. It can affect the scalp or entire body and may be temporary or permanent. Causes include genetics, autoimmune diseases, hormonal changes, stress, or underlying medical conditions."
Types of Alopecia
- Alopecia Areata: Autoimmune disorder causing patchy hair loss. Can affect scalp, beard, eyebrows, or body hair.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Genetic pattern baldness in men and women due to hormone (DHT) sensitivity.
- Telogen Effluvium: Temporary shedding due to stress, illness, or hormonal changes. Often reversible.
- Traction Alopecia: Caused by tight hairstyles pulling on hair. Preventable with early care.
- Cicatricial Alopecia (Scarring): Inflammatory scalp disorders that destroy hair follicles and lead to permanent loss.
Treatment Options
| Condition | Common Treatments |
|---|---|
| Alopecia Areata | Corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy |
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Minoxidil, Finasteride, PRP therapy, Hair transplant |
| Telogen Effluvium | Resolves on its own, treat underlying cause |
| Traction Alopecia | Hairstyle modification, early intervention |
| Scarring Alopecia | Anti-inflammatory drugs, early diagnosis essential |
Diagnosis
- Medical history and scalp examination
- Pull test to check hair fragility
- Blood tests: thyroid, iron, vitamin D, hormonal levels
- Scalp biopsy in suspected scarring alopecia
- Dermatoscopy for detailed follicle analysis
Prevention & Self-Care
- Avoid tight hairstyles and heat/chemical treatments
- Manage stress with healthy coping mechanisms
- Eat a protein-rich, balanced diet with iron and vitamins
- Keep scalp clean; treat dandruff or psoriasis promptly
When to See a Doctor?
- Sudden or patchy hair loss
- Scalp is red, itchy, or painful
- Persistent shedding after illness or childbirth
- Family history of early hair loss and visible signs appearing
Medicine Use Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes and does not replace medical advice. Please consult a dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment.
