Eczema
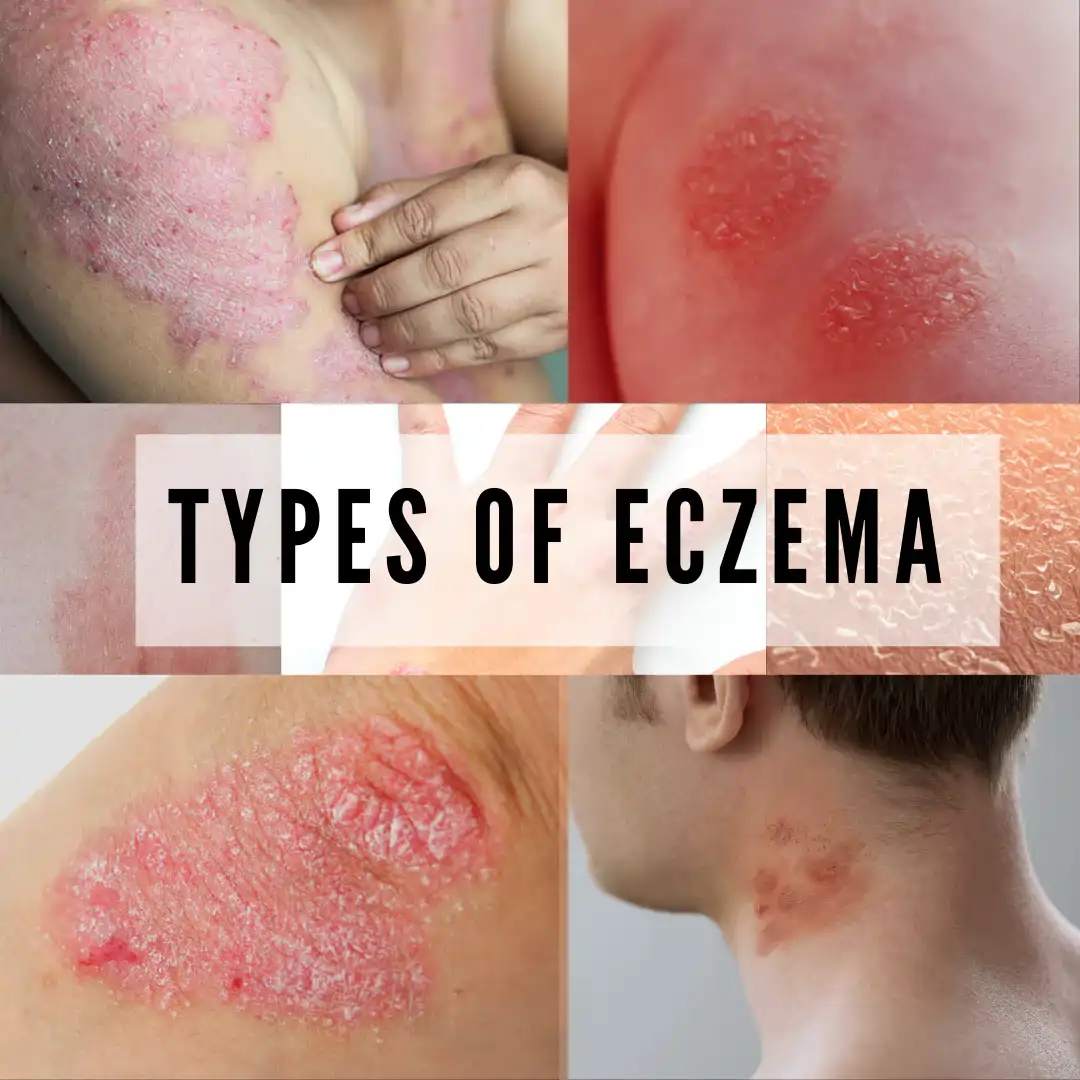
Eczema
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common, chronic skin condition characterized by dryness, redness, itching, and inflammation. It often starts in childhood but can affect individuals of any age. Eczema is not contagious, but it can severely impact the quality of life due to persistent discomfort and visible skin changes.
What's Included
Dermatologist’s Perspective:
- Cause: Eczema is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that affect the skin’s barrier function and immune response.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: People with eczema have a weakened skin barrier, making their skin more prone to moisture loss and irritants.
- Allergy Link: Eczema often occurs alongside other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever (known as the atopic triad).
Common Triggers
- Dry weather or low humidity
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander)
- Heat and sweating
- Stress and emotional triggers
- Certain fabrics like wool or synthetic materials
Symptoms of Eczema
- Intense itching (often worse at night)
- Red to brownish-gray patches on the skin
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Thickened, leathery skin from chronic scratching
- Oozing or crusting in severe cases
Diagnosis
-
Eczema is diagnosed clinically by a dermatologist based on patient history and skin examination. Allergy testing may be recommended if triggers are suspected.
Treatment Options
- Moisturizers: Regular use of fragrance-free emollients helps restore the skin barrier.
- Topical steroids: Reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Non-steroid creams used for sensitive areas like the face.
- Antihistamines: Help control itching and allergic reactions.
- Phototherapy: UV light therapy for chronic or widespread eczema.
- Biologics: For moderate-to-severe cases unresponsive to other treatments (e.g., dupilumab).
Important Notes
- Eczema is not contagious.
- Proper skin care and trigger avoidance are crucial for long-term control.
- Early dermatological intervention can prevent complications like skin infections.
Medicine Use Disclaimer: The information provided on this page is for general educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
Do not use any medication without consulting a qualified dermatologist or healthcare professional.
Individual diagnosis and treatment plans may vary based on personal health history and specific conditions.
